In a vast and mysterious universe, the absence of gravity triggers amazing and unique phenomena. One of them is the behavior of fire in weightlessness, a fascinating topic that has captured the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts alike. In this article, we explore how fire works in a zero-gravity environment, revealing the floating dance of science that defies our conventional expectations.
Fire, at its core, is a chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidizer, which usually occurs on Earth in the presence of oxygen. However, in space, where gravity is almost nonexistent, flames take on a different appearance and behavior.
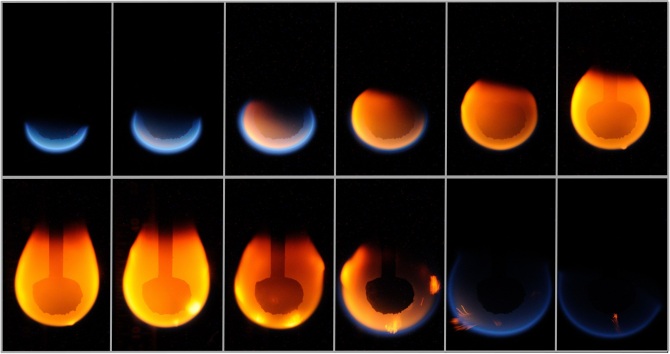
When a flame is ignited in weightlessness, the fire does not rise as it would on Earth, forming a characteristic conical shape. Instead, the flames acquire an almost perfect sphere. This is because without gravity to pull the hot gases up, the flame has no preferred direction of propagation.
The absence of gravity also has a significant effect on the combustion process. On Earth, the oxygen needed for fire is supplied by the surrounding air. However, there is no air in space. Therefore, for fire to sustain itself, an independent supply of oxygen is required. In experiments carried out on the International Space Station, special devices are used to provide controlled oxygen to the flames.
(Photo: NASA)
In addition to shape and oxygen delivery, weightless fire has other characteristics. As fuel particles, liquids or solids, they do not fall to the ground in space, meaning they can float freely in the environment. This can lead to unusual behavior such as the formation of airborne fuel droplets. These bubbles may burn slowly or split into many smaller flames, creating a unique display.
The study of weightless fire has not only scientific and aesthetic appeal but also important practical implications. Understanding how fires behave in space will help improve safety on manned space missions and help design more efficient fire suppression systems.
Additionally, the study of fire in weightlessness may have terrestrial applications. By removing the effect of gravity, scientists can gain a better understanding of combustion processes and use that knowledge to improve the efficiency of engines and combustion systems on Earth.